Phonology
We have first to get the meaning of the word Phonology which is the study of how sounds are organized and used in natural languages, as I remember it includes phonetics and phonemics. Pretty easy right! Well, phonology is so big, that it usually needs to be taken in bite-sized portions in order to be approached at all. One of the bigger pieces that people take out of the phonology pie in order to cut up even further is one called "phonetics." Before you read about phonetics though, stop to think about all the movements your whole body goes through in order to create the sounds you use in a sentence. Feel your diaphragm undulate, your tongue move and swell, your lips twitch, your lungs fill and empty themselves, your larynx vibrate, even your nose hold sounds for tiny moments. If you put all of that together, you get a glimpse at what phonology is about. Understanding how speech sound are made helps linguists figure out where languages came from and where they are going; it helps scientists program computers to comprehend and mimic human speech; and it might even help you learn a new language.
Phonetics
Phonetics is primarily used to describe the way sounds are written and how written words are perceived as sounds. If you look at the definition, you can see how there's overlap with that of "phonology." That overlap in definition can be a source of confusion for some, but there's no reason to let it ruin your day. For most people the only reason they will ever need phonetics to use the International Phonetic Alphabet, which is really only usable to a select few. It's a way of standardizing the pronunciation of words from any language so that, theoretically, anyone reading any word in any language can at least pronounce it properly. Phonetics has three main branches:
Articulatory phonetics: is concerned with the positions and movements of the speech organs such as the lips and the tongue in producing sound.
Acoustic phonetics: is concerned with the physical properties of the sound waves.
Auditory phonetics: is concerned with the perception of the speech sounds or the effect on the ear.
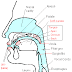
Speech organs picture 1 below.
My group did the tongue twister:
1. Lesser weather never weathered lesser wetter weather.
/lɛsə wɛðə nɛvə wɛðərd lɛsə wɛtə wɛðər/
2. Big black bugs bleed blue black blood but baby bugs bleed blue blood.
/bɪg blæk bəgz bli:d blu: blæk bləd bət beɪbi bəgz bli:d blu: bləd/
3. King thistle stuck a thousand thistles in the thistle of his thumb. A thousand thistles king thistle stuck in the thistle of his thumb. If king thistle stuck a thousand thistles in the thistle of his thumb, how many thistles did king thistle stick in the thistle of his thumb?
/kɪŋ θɪsəl stək ə θawzənd θɪsəlz ɪn ðə θɪsəl əv hɪz θəm. ə θawzənd θɪsəlz kɪŋ θɪsəl stək ɪn ðə θɪsəl əv hɪz θəm. ɪf kɪŋ θɪsəl stək ə θawzənd θɪsəlz ɪn ðə θɪsəl əv hɪz θəm, haw mɛni θɪsəlz dɪd kɪŋ θɪsəl stɪk ɪn ðə θɪsəl əv hɪz θəm?/
INITIAL MEDIAL FINAL
1.
Ball, tall
Babble, battle
Cab, cat
/Bɒl, tɒl /
/bæbəl, bætəl/
/kæb, kæt/
2.
Bow, pow
Stable, staple
lab, lap
/bau, pau/
/stebəl stepəl/
/læb læp/
3.
Deed, need
Tidy, tiny
Bad, ban
/did, nid/
/taɪdi, taɪni/
/bæd, bæn/
4.
Die, lie
Tiding, tiling
Pad, Pal
/daɪ, laɪ/
/taɪdɪŋ, taɪlɪŋ/
/Pæd, Pæl/
5.
Pie, tie
Topper, totter
Hip, hit
/paɪ, taɪ/
/tɑpər, tɑtər/
/hɪp, hɪt/